Internet of Things (IOT)
The Internet of Things (IoT) refers to the network of interconnected physical devices, vehicles, appliances, and other objects embedded with sensors, actuators, software, and network connectivity.
These devices collect and exchange data with each other through the Internet, enabling them to communicate and perform tasks without direct human intervention. The goal of IoT is to create a seamless and intelligent network of smart devices that enhance efficiency, convenience, and automation in various domains.
Advantage @DGU
- Dehradun - A Safe, Beautiful & Cosmopolitan Education City.
- Bundle of Industry Integrated Value Added Certificates.
- Students from 23 States & 5 Countries on campus.
- Multiple Placements for all.
- More than 350+ Companies for Campus Placement.
- Possibilities of International Exposure.
- Separate in campus Girls & Boys hostels with Modern Sporting & Gym facilities.
Level & Duration
Level
Certificate

Duration
1 Year

Key Concepts
Sensors and Actuators
IoT devices are equipped with sensors to collect data from the surrounding environment (temperature, humidity, motion, etc.) and actuators to perform actions based on the collected data.
Connectivity
Devices in the IoT ecosystem communicate with each other through wired or wireless networks. Common communication protocols include MQTT, CoAP, HTTP, and more.
Data Processing and Analytics
Collected data is processed and analyzed either locally on the device or in the cloud. Machine learning and analytics algorithms help derive meaningful insights from the vast amounts of IoT-generated data.
Cloud Computing
Cloud platforms are often used to store and process IoT data. Cloud services provide scalability, storage, and computational resources for managing large-scale IoT deployments.
Edge Computing
In edge computing, data processing occurs closer to the source (on the device or in a local gateway) rather than relying solely on centralized cloud servers. This reduces latency and enhances real-time processing capabilities.
Security
Security is a critical consideration in IoT due to the interconnected nature of devices. Measures such as encryption, secure authentication, and regular software updates are implemented to protect IoT ecosystems.
Interoperability
Standardization and interoperability protocols ensure that different IoT devices and platforms can communicate and work together seamlessly.
IoT Platforms
IoT platforms provide a framework for connecting, managing, and securing IoT devices. They often include features for data storage, analytics, device management, and application development.
Applications of IoT
Smart Home
Home automation systems, smart thermostats, connected appliances, and security systems.
Industrial IoT (IIoT)
Monitoring and optimizing industrial processes, predictive maintenance, and supply chain management.
Healthcare
Remote patient monitoring, wearable health devices, and smart medical equipment.
Smart Cities
Traffic management, waste management, public safety, and environmental monitoring.
Agriculture
Precision farming, crop monitoring, and livestock tracking.
Retail
Inventory management, customer tracking, and personalized shopping experiences.
Transportation
Connected vehicles, smart traffic management, and fleet tracking.
Energy Management
Smart grid systems, energy consumption monitoring, and optimization.
Environmental Monitoring
Air quality monitoring, water quality monitoring, and disaster response.
Challenges and Considerations
Security and Privacy Concerns
Protecting IoT devices and data from cyber threats and ensuring user privacy are ongoing challenges.
Interoperability
Standardizing protocols to enable seamless communication between diverse IoT devices and platforms.
Scalability
Managing the increasing number of connected devices and the growing volume of data generated by IoT ecosystems.
Power Consumption
Addressing power constraints in IoT devices, especially those powered by batteries.
Data Management
Efficiently handling, processing, and storing large volumes of data generated by IoT devices.
Regulatory Compliance
Adhering to regulations and standards related to IoT security, privacy, and data protection.
The Internet of Things has the potential to transform various industries, improve efficiency, and enhance the quality of life. As IoT technologies continue to evolve, addressing challenges and ensuring secure, interoperable, and scalable implementations will be crucial for widespread adoption and success.
Placements
Enjoy Everyday while Ensuring Great Career

Thanks to DGU’s mock interviews, value‑added courses, and hands‑on projects I developed confidence, communication skills and real-world business sense. The practical exposure and industry-aligned learning helped me step into Indigo Paints Limited ready to perform and grow.

From engaging campus activities to hands-on projects, DGU made learning practical and exciting. This experience helped me step into Reliance Retail ready to make an impact.

One thing that really helped me during the placement season was the confidence I gained from the mock sessions. My professors pointed out mistakes I hadn’t even realized I was making and gave me valuable tips that made the process smoother. This foundation prepared me well for my role at Asian Paints Ltd.

The mix of interactive learning, practical projects, and expert guidance shaped my skills effectively. It gave me the confidence to start my professional journey with Tech Mahindra.

Hands-on learning, value-added courses, and supportive faculty prepared me for real-world challenges. These experiences helped me confidently join Hafele India Pvt Ltd and contribute from day one.

DBS Global University’s rigorous learning environment and hands-on experiences challenged me to grow constantly. This preparation gave me the confidence and skills to step into Grant Thornton Bharat LLP with readiness.

DBS Global University’s competitive and dynamic environment pushed me to perform at my best every day. This energy, combined with practical learning and guidance from faculty, helped me secure my role at MyGetWellStore.

DBS Global University’s practical projects and faculty guidance helped me build real-world skills and confidence. This preparation enabled me to step into Prism Johnson ready to contribute effectively.

At DBS Global University, engaging in practical projects and hands-on learning enhanced my skills and confidence, equipping me to step into my role at Phronesis Partners with clear direction and focus.

Through DBS Global University’s hands-on projects and skill-focused sessions, I gained practical experience and strengthened my confidence. These opportunities equipped me to make meaningful contributions at Digital Marveled Private Limited.

DGU helped me grow into someone who can take on challenges with confidence and clarity. My placement at Extramarks Education feels like the right step toward building a meaningful career.

DGU shaped my skills through constant guidance, practical exposure, and a supportive environment. Getting placed at High Beam Global feels like a strong beginning to my professional journey.
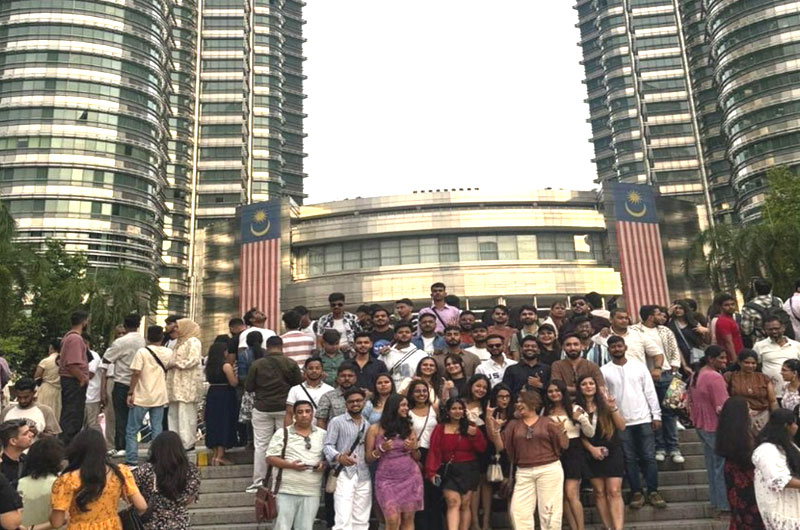
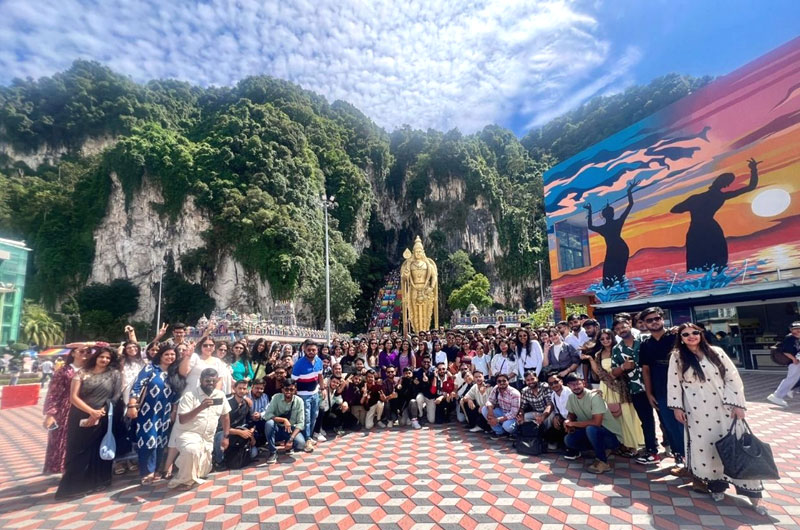
Student Education Immersion Program
Study Abroad Opportunities for Global Careers
DBS Global University offers students flexible and impactful study abroad pathways designed to build global competence and career readiness. Backed by a strong network of 50+ MOUs across 20+ countries, the University enables meaningful international exposure through Short-Term Global Immersion Programs, Credit Transfer Study Abroad Programs, and Dual Degree & Long-Term Global Pathways.
Through strategic partnerships with institutions across Australia, USA, Europe, Malaysia, Singapore, Dubai, Thailand, Indonesia, Turkey, Hong Kong and Russia, students benefit from internationally benchmarked curricula, industry exposure, multicultural classrooms, and cross-cultural learning. These experiences integrate academics with experiential learning, global networking, and real-world insights—empowering students with a global mindset, enhanced employability, and the skills required for successful international careers.